Cymbopleura anglica
-
Category
-
Length Range39-52 µm
-
Width Range13.0-18.2 µm
-
Striae in 10 µm10-12 on the dorsal side in the valve center, slightly higher density on ventral side and near apices
-
Reported AsCymbella naviculiformis (Patrick and Reimer 1975, p. 31)
-
ContributorLoren Bahls - Jul 2012
-
ReviewerSam Rushforth - Aug 2012
Identification
Description
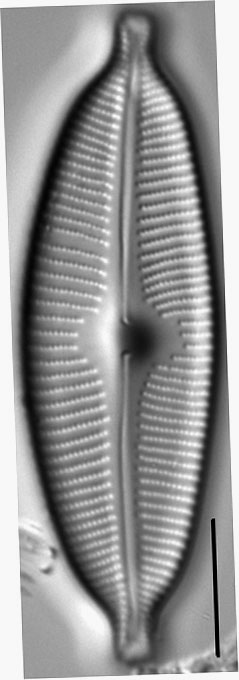
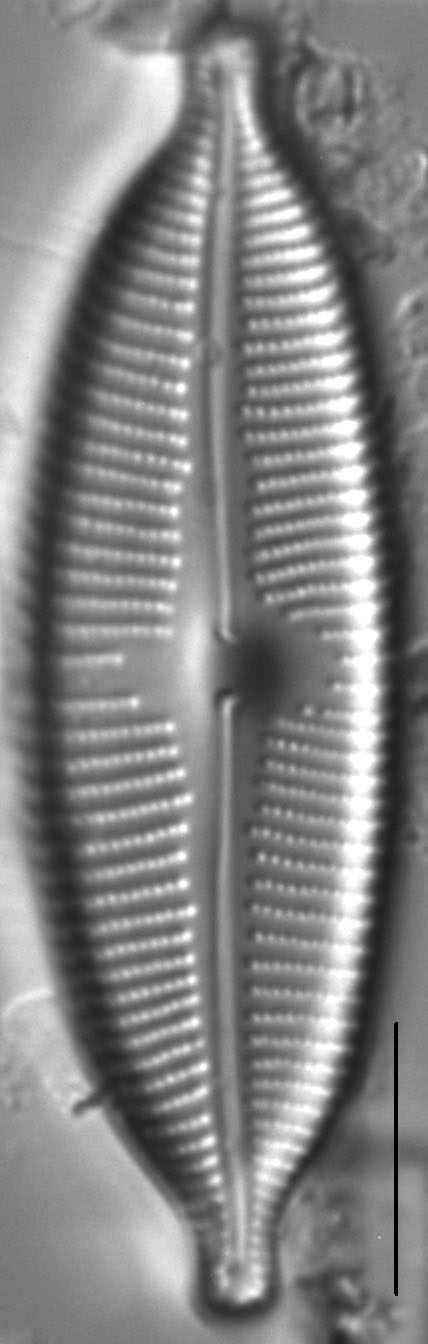
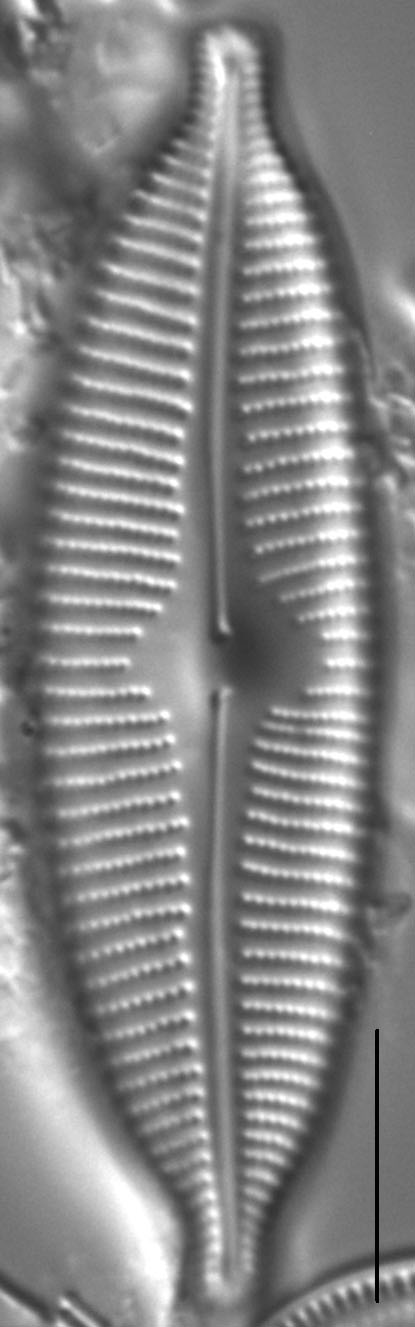
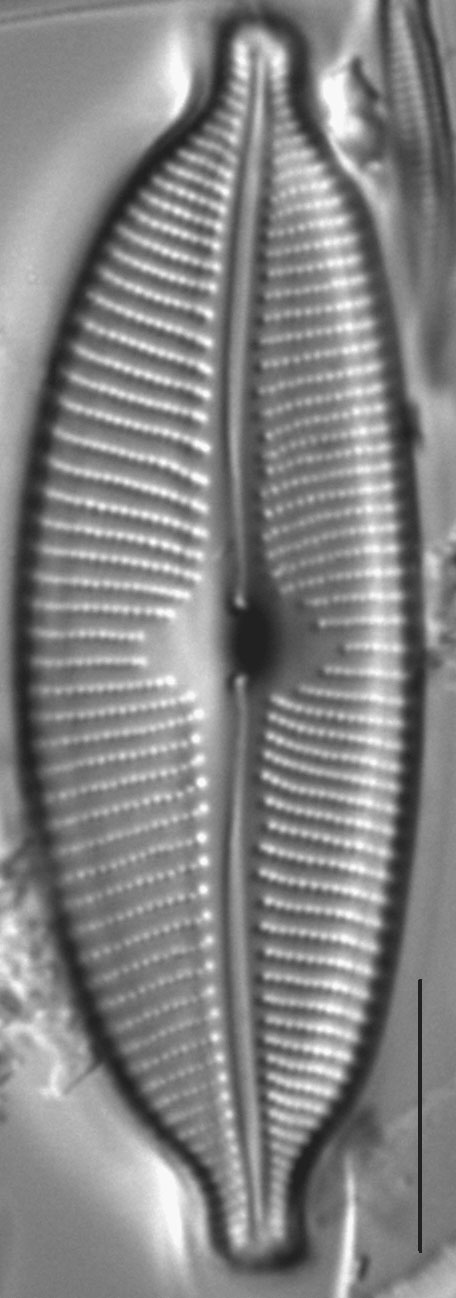
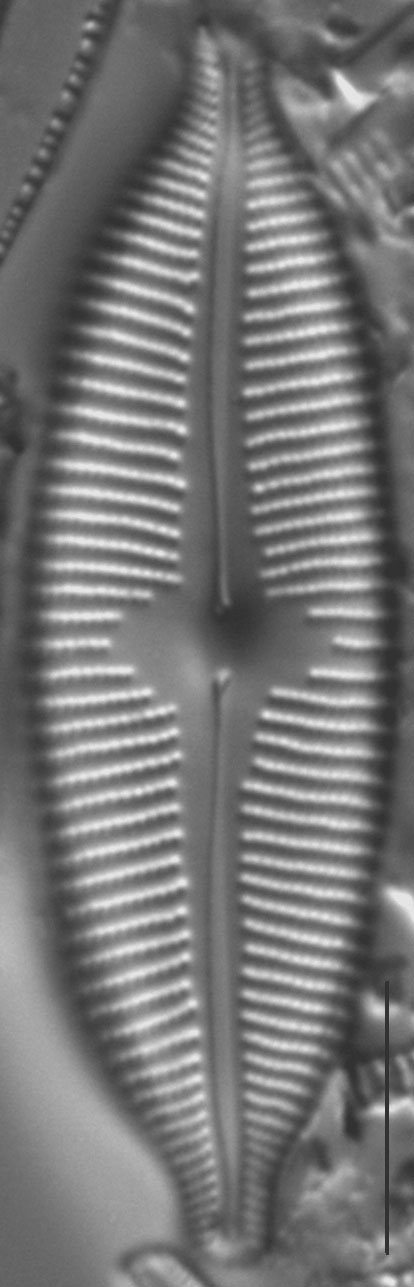
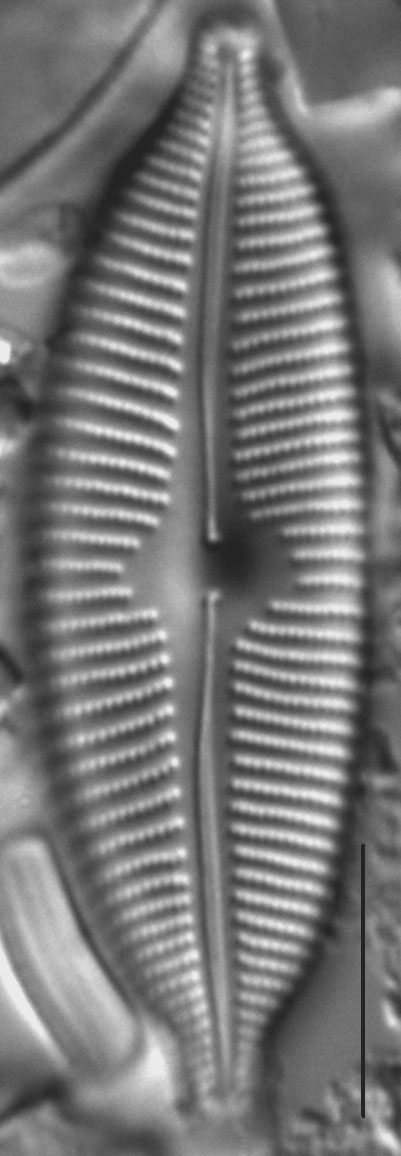
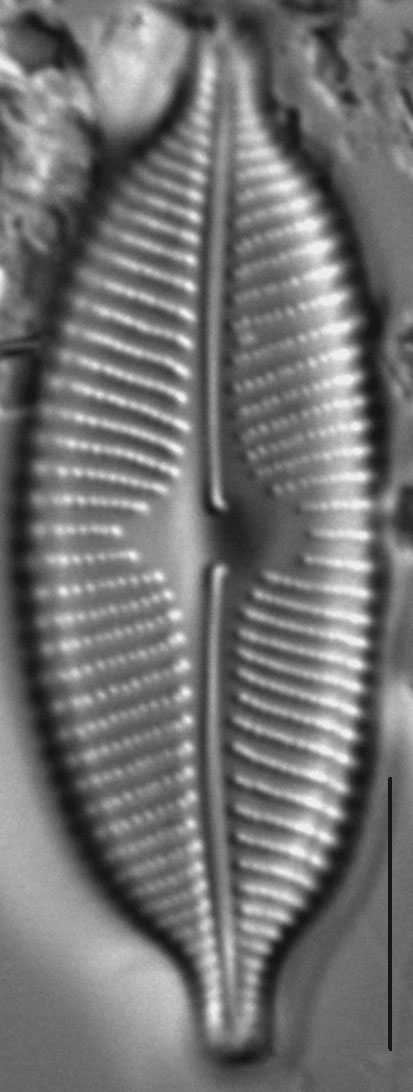
Valves are elliptic and slightly to moderately dorsiventral. Apices are rostrate to subcapitate and bluntly rounded. The axial area is narrow and expands gradually towards a large, rounded central area. The raphe is lateral and becomes filiform near the proximal ends, which are somewhat inflated and deflected toward the ventral margin. Distal raphe ends are deflected dorsally. Striae are slightly radiate throughout the valve and somewhat more closely spaced on the ventral side and near the apices. Areolae are easily resolved in LM and number 24-28 in 10 µm.
Autecology
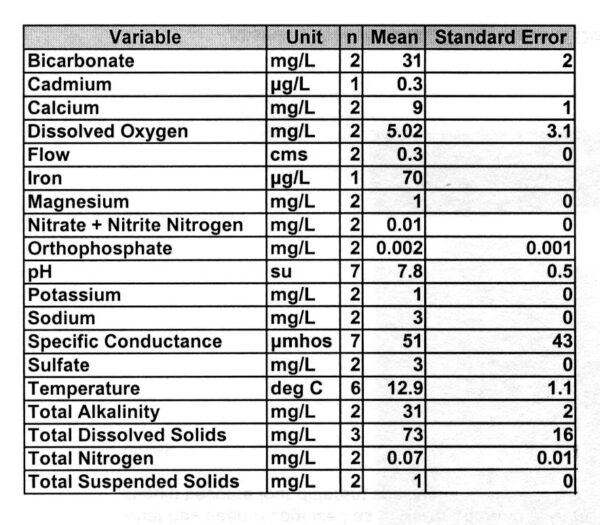
Cymbopleura anglica is uncommon in lakes and ponds and in streams below lakes and ponds in the northern Rocky Mountains of Idaho and western Montana. Here it prefers cool and somewhat alkaline oligotrophic waters with low electrical conductance (see table below). Krammer (2003) reports this species as widely distributed in nordic-alpine and subarctic areas of Europe, where it prefers oligotrophic waters with lower electrolyte content.
-
Size Range, µm3
-
Motility
-
Attachment
-
Habitat
-
Colony
-
Waterbody
- Learn more about this
Original Description
-
BasionymCymbella anglica
-
AuthorLagerstedt 1873
Citations & Links
Citations
Links
-
Index Nominum Algarum
-
North American Diatom Ecological DatabaseNADED ID: 44599
Cite This Page
Bahls, L. (2012). Cymbopleura anglica. In Diatoms of North America. Retrieved April 19, 2024, from https://diatoms.org/species/cymbopleura_anglica
Responses
The 15 response plots show an environmental variable (x axis) against the relative abundance (y axis) of Cymbopleura anglica from all the stream reaches where it was present. Note that the relative abundance scale is the same on each plot. Explanation of each environmental variable and units are as follows:
ELEVATION = stream reach elevation (meters)
STRAHLER = distribution plot of the Strahler Stream Order
SLOPE = stream reach gradient (degrees)
W1_HALL = an index that is a measure of streamside (riparian) human activity that ranges from 0 - 10, with a value of 0 indicating of minimal disturbance to a value of 10 indicating severe disturbance.
PHSTVL = pH measured in a sealed syringe sample (pH units)
log_COND = log concentration of specific conductivity (µS/cm)
log_PTL = log concentration of total phosphorus (µg/L)
log_NO3 = log concentration of nitrate (µeq/L)
log_DOC = log concentration of dissolved organic carbon (mg/L)
log_SIO2 = log concentration of silicon (mg/L)
log_NA = log concentration of sodium (µeq/L)
log_HCO3 = log concentration of the bicarbonate ion (µeq/L)
EMBED = percent of the stream substrate that is embedded by sand and fine sediment
log_TURBIDITY = log of turbidity, a measure of cloudiness of water, in nephelometric turbidity units (NTU).
DISTOT = an index of total human disturbance in the watershed that ranges from 1 - 100, with a value of 0 indicating of minimal disturbance to a value of 100 indicating severe disturbance.
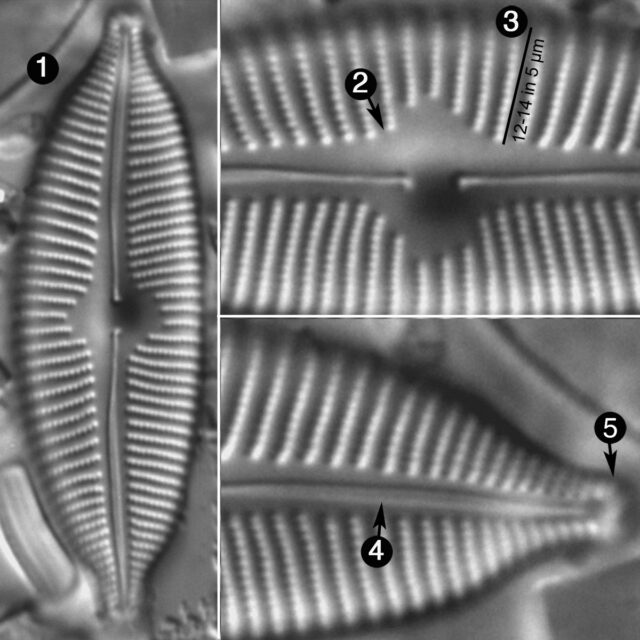
Cymbopleura anglica
- Valves elliptic
- Central area large
- Areolae 24-28 in 10 µm
- Raphe lateral
- Apices bluntly rounded
Valves are moderately large, elliptic and somewhat dorsiventral, with bluntly rounded apices. The central area is large. The raphe is lateral, becoming filiform near the proximal and distal ends. Areolae in the striae are easily resolved in LM and number 24-28 in 10 µm.
 Diatoms of North America
Diatoms of North America